AFUE Rating Explained: What is a good AFUE Rating?
A furnace’s Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating indicates how efficient the furnace is at heating over time. This determines how much fuel it needs to heat your home and can save you money on your energy bill.
AFUE ratings are measured between 0-100%. A higher AFUE means that the furnace will be more efficient with the combustion gases it uses, which will cost less in energy bills for your household.
AFUE ratings are measured between 0-100%. A higher AFUE means that the furnace will be more efficient with the combustion gases it uses, which will cost less in energy bills for your household.
What is a Good AFUE Rating?
The minimum AFUE rating allowed by the Department of Energy is 80% which means that 8/10 of every BTU used to run the furnaces goes to heating your home.
Generally, mid-efficiency rated furnaces have an AFUE rating between 90% to 93%.
High efficiency furnaces have an AFUE ratings from 95% to 98%.
Systems with higher energy efficiency are condensing furnaces that condense and convert escaped water vapors into energy and heat. Because of this, high efficient furnaces require different exhaust than an 80% furnace.
Bottom Line: The higher the AFUE rating the more efficient the heating furnace burns and the less money you will spend to heat your home.
Generally, mid-efficiency rated furnaces have an AFUE rating between 90% to 93%.
High efficiency furnaces have an AFUE ratings from 95% to 98%.
Systems with higher energy efficiency are condensing furnaces that condense and convert escaped water vapors into energy and heat. Because of this, high efficient furnaces require different exhaust than an 80% furnace.
Bottom Line: The higher the AFUE rating the more efficient the heating furnace burns and the less money you will spend to heat your home.
Are High AFUE Furnaces Worth it?
High-efficiency furnaces offer significant benefits in terms of energy savings, environmental impact, and heating efficiency, but they come with higher initial installation costs.
A high-efficiency furnace is worth the higher price if you plan to stay in the home a long time and if you live in a climate with cold winters. The average high-efficiency furnace, also called a condensing furnace, cost more to buy and install than the average conventional noncondensing furnace. However, a high efficiency model accrues significant savings over time since it requires less energy to operate.
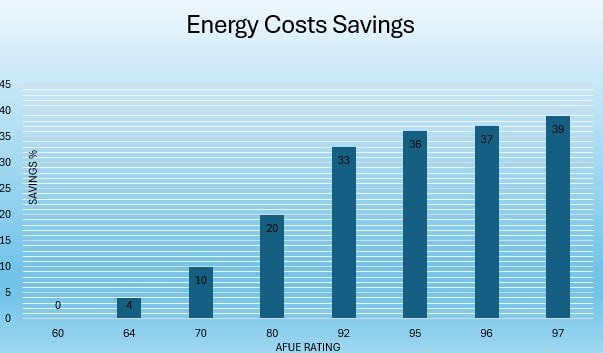
A good way to think about it is to take your current furnaces AFUE and subtract that from the new furnaces AFUE and you will roughly get your savings amount by upgrading to a high efficient furnace. For example, if you have an 80% furnace and you are installing a 95% furnace, your energy savings would be about 15%.
Chances are that if you have an older 80% furnace than it is probably not running as efficiently as it did at the beginning of its life. Then the cost savings would even be higher.
High efficient furnaces also have different gas valves (2 stage and modulating) and blower motors (ECM and Variable Speed) that can make them even more efficient than an older standard, single stage furnace.
A high-efficiency furnace is worth the higher price if you plan to stay in the home a long time and if you live in a climate with cold winters. The average high-efficiency furnace, also called a condensing furnace, cost more to buy and install than the average conventional noncondensing furnace. However, a high efficiency model accrues significant savings over time since it requires less energy to operate.
A good way to think about it is to take your current furnaces AFUE and subtract that from the new furnaces AFUE and you will roughly get your savings amount by upgrading to a high efficient furnace. For example, if you have an 80% furnace and you are installing a 95% furnace, your energy savings would be about 15%.
Chances are that if you have an older 80% furnace than it is probably not running as efficiently as it did at the beginning of its life. Then the cost savings would even be higher.
High efficient furnaces also have different gas valves (2 stage and modulating) and blower motors (ECM and Variable Speed) that can make them even more efficient than an older standard, single stage furnace.